Zoonotic diseases that are transmitted from guinea fowl to humans. Chlamydiosis: an unusual bacteria-like organism, occurs worldwide and affects more than 100 avian species including guinea fowl. It causes a disease called psittacosis and the disease is called ornithosis when diagnosed in all other birds or in humans. Chlamydiosis is primarily transmitted by inhalation of contaminated fecal dust and is spread by carrier birds, which act as the main reservoirs for the disease. The organism is excreted in both the feces and nasal secretions. Shedding is sporadic and is usually induced by stress. A carrier state can persist for years. The organism survives drying, which facilitates oral spread and allows transmission on contaminated clothing and equipment. Chlamydiosis can be transmitted bird to bird, feces to bird, and bird to human. Human to human transmission can occur, mainly by exposure to patient's saliva. Salmonellosis: There are approximately 200 different serotypes of Salmonella species. Most animals are susceptible to salmonella infection. This bacterial disease occurs most frequently in stressed individuals. Many infections are subclinical. Common clinical symptoms in all species include diarrhea, vomiting, and a low-grade fever. Infections can progress to dehydration, weakness, and sometimes, especially in the very young or very old, death. In severe cases there can be a high fever, septicemia (blood poisoning), headaches, and an enlarged painful spleen. Focal infections may occur in any organ, including heart, kidney, joints, meninges (membranes which surround and protect the brain and spinal cord), and the periosteum (fibrous membrane of connective tissue which closely surrounds all bones except at the joints). Avian Tuberculosis: Avian tuberculosis is caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium avium which is closely related to the human and bovine tuberculosis bacteria. In birds, M. avium causes a chronic debilitating disease with tubercular nodules. In humans, M. avium infections can cause local wound infections with swelling of regional lymph nodes. The infection is most severe in immunocompromised individuals. M. avium is spread by ingestion of food or water contaminated by feces from shedder birds. Tuberculous poultry flocks should be depopulated. Histoplasmosis: Certain fungi prefer to grow in soils enriched with avian manures. Histoplasma capsulatum is one of these. The fungus is also associated with construction sites and caves. Birds are not susceptible to infection, but histoplasmosis can affect humans, dogs, cats, cattle, sheep, horses, and many wild mammals. This is only 4 of many zoonotic diseases | Common diseases for guinea fowl to get: Coccidiosis infection- Coccidiosis is caused in poultry by a one-celled parasite of the genus Eimeria. The life cycle of Eimeria takes about four to seven days to complete. It begins when active 'oocysts' are picked up by the bird and swallowed. An 'oocyst' is a capsule with a thick wall protecting the parasites. They 'sporulate' or become infective if moisture, temperature, and oxygen become conducive to growth. After a bird eats the oocysts, coccidia imbed in the intestinal lining and multiply several times, damaging tissue. Roundworms- Hair worms - Found in the crop, oesophagus, proventriculus and intestine. 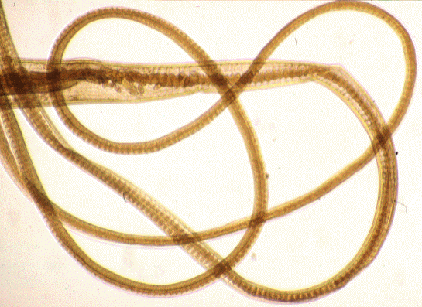 |